Battery Energy Storage
At the core of battery energy storage space lies the basic principle of converting electrical power into chemical energy and, afterward, back to electric power when needed. One of the fundamental principles behind the performance of battery storage space systems is their ability to store excess power generated during periods of reduced need and launch it during peak need. This capacity is essential for maintaining the security and reliability of the power grid, particularly as eco-friendly power sources like solar and wind are progressively integrated into our energy mix. By keeping surplus energy, battery storage space systems can minimize the intermittency of eco-friendly power, ensuring a consistent and reputable power supply.
Just How Battery Storage Space Works
At the core of battery energy storage space lies the basic principle of converting electrical power right into chemical energy and, after that, back to electric power when needed. This procedure is helped with by the elaborate operations of batteries, which contain 3 main parts: the anode, cathode, and electrolyte.
The anode and cathode are the positive and negative electrodes, specifically where the power exchange happens. The electrolyte is the tool that allows ions to move between the anode and cathode, thus making it possible for the circulation of electricity to exist. Electric power is related to the battery when a battery is charging, triggering ions to move from the cathode to the anode. Conversely, these ions return to the cathode during discharge, releasing electrical power that can be used to power various applications.
This process can be described through the following stages:
| Stage | Refine |
|---|---|
| Billing | Electric energy is transformed into chemical energy as ions move from the cathode to the anode. |
| Discharging | Chemical energy is transformed into electric energy as ions move from the anode to the cathode. |
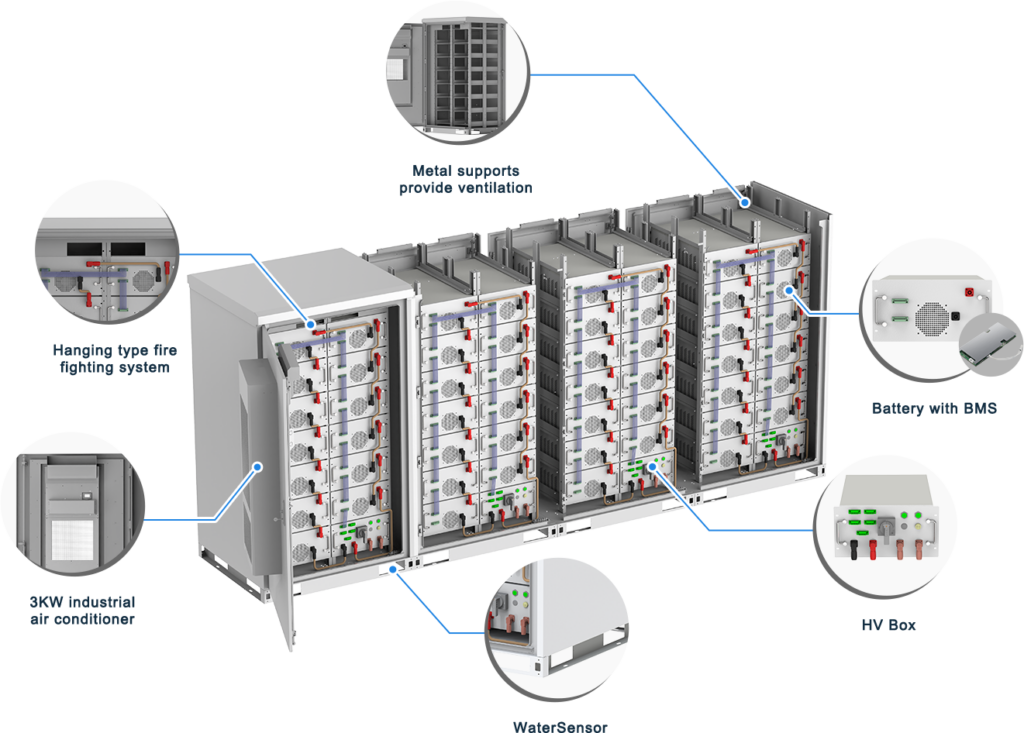
Components of a battery energy storage system typically include small parts such as a battery system, a power conversion system or inverter, a battery management system, environmental controls, controllers, and safety equipment (e.g., fire extinguishers, sensors, and alarms).

Relevance of Battery Energy Storage
Battery energy storage plays a vital role in modern energy systems, providing a reliable and efficient way to store energy for numerous applications. With the popularity of renewable energy sources such as solar and wind, the need for efficient energy storage space solutions is at an all-time high. Battery storage systems ensure a constant and stable energy supply by capturing excess energy generated during peak production periods and utilizing it during high demand or reduced production periods.
Increased reliability and durability of the grid
By storing power, batteries can maintain connectivity to critical frameworks and solutions by providing backup power in case of failure or disruption. This capability is critical in areas prone to natural disasters or in areas with aging grid facilities.
Grid Connection.
Eco-friendly energy resources are naturally variable, with their output changing depending on climatic conditions and the time of day. Battery storage space systems smooth out these fluctuations, storing excess energy when manufacturing is high and releasing it when manufacturing is low. Not only does this capitalize on renewable energy sources, but it also helps maintain the grid and reduces dependence on non-renewable energy sources.
Significant savings
By maintaining energy when demand decreases and costs are low and releasing energy when demand peaks and costs are high, businesses and energy companies can maximize energy use and minimize costs. Battery storage can also delay or eliminate the need for costly facility upgrades, such as new power plants or transmission lines, by managing loads and providing additional capacity.
Ecological Advantages
Battery energy storage systems reduce greenhouse gas emissions. By increasing the penetration of renewable energy sources and minimizing reliance on fossil-fueled nuclear power plants, batteries help reduce the carbon impact of the electricity sector. This shift to cleaner energy is critical to mitigating the effects of environmental adjustments and promoting lasting growth.
Storage
It is also essential for the development of decentralized energy systems and microgrids. These systems can generate and store energy on-site, reducing reliance on centralized nuclear power plants and large-scale grid frameworks, thereby increasing power safety, security, and resilience. This is particularly helpful in remote or off-grid areas where conventional energy supplies may be unreliable or unavailable.
It is a crucial enabler for a versatile, reliable, and long-lasting energy future that sustains widespread adoption of renewable energy sources, improves grid security, and provides economic and environmental advantages. As innovation continues to advance, battery storage capabilities in the energy sector will undoubtedly continue to expand, driving even more progress and innovation in energy monitoring and sustainability.
Advantages of Battery Energy Storage Devices
Battery energy storage systems are an essential part of contemporary power monitoring. These systems’ versatility, performance, and reliability are crucial to meeting property and industrial energy needs. Below, we look at the key advantages of applying battery energy storage space solutions.
Increased grid security
One of the critical benefits of battery storage systems is their ability to improve grid security. By retaining excess energy during periods of reduced demand and releasing it during peak demand, these systems help to balance the tonnage of the grid, reducing the threat of blackouts and ensuring a steady supply of electricity.
Peaking
By storing energy during low-demand periods and releasing it during high-demand periods, BESS can help reduce the grid’s electricity demand during peak hours. This “peaking” minimizes the need for expensive peak power plants, often powered by fossil fuels, resulting in cost and environmental benefits.

Energy arbitrage
With the ability to store energy when prices are low and dispatch it when prices are high, BESS can enable energy arbitrage, potentially saving significant amounts of money or generating additional revenue streams.
Increased utilization of renewable resources
Battery energy storage systems facilitate the penetration of renewable energy into the energy mix by storing electricity generated from renewable sources such as solar and wind. This reduces dependence on non-renewable fuels, lowers greenhouse gas emissions, and promotes environmental sustainability.
Energy independence and integrity
For home and business individuals, battery storage space systems provide a form of electrical self-sufficiency and reliability. During a power outage, these systems can act as a backup power source, ensuring uninterrupted operation of critical functions.
Assisting in remote and off-grid areas
Battery storage space systems are essential in remote and off-grid areas. These systems efficiently use locally generated renewable energy and minimize the need for expensive and polluting diesel generators.
| Advantages | Summary |
|---|---|
| Grid Stability | Equilibriums load, decreases power outages |
| Cost Savings | Peak shaving, reduced energy bills |
| Renewable Energy Assimilation | Facilitates higher eco-friendly penetration |
| Power Self-reliance | Supplies backup power during outages |
| Support for Remote Locations | Reduces reliance on diesel generators |
Types of Battery Energy Storage
There are several types of battery energy storage systems, each with unique features and applications. Understanding the types of battery energy storage is critical to choosing the best technology for your specific needs.
Lithium-Ion Batteries
Lithium-ion batteries are the most common type of battery storage because of their high energy density, long cycle life, and low price. They are commonly used in domestic and industrial applications and electric vehicles. These batteries can store large amounts of energy in a reasonably small volume, making them ideal for limited space.
Lead Acid Batteries
Lead-acid batteries were one of the earliest forms of battery storage. They are known for their reliability and low cost, making them ideal for applications with limited budgets. Despite their lower power density and shorter life expectancy than lithium-ion batteries, lead-acid batteries are still used in uninterruptible power supply products (UPS) and backup power systems.
Nickel-Cadmium Batteries
Nickel-cadmium (NiCd) batteries are known for their durability and ability to operate in extreme temperatures. NiCd batteries have a longer life span than lead-acid batteries and are commonly used in aviation and industrial applications. However, the popularity of cadmium batteries has declined due to the ecological impact of cadmium toxicity.
Fluid Flow Batteries
Fluid flow batteries (e.g., vanadium redox cycle batteries) are characterized by their ability to provide virtually unlimited energy through a fluid electrolyte in an external container. They are particularly well suited for large-scale energy storage space applications such as grid stabilization and renewable energy absorption. Their long cycle life and scalability make them a promising innovation for utility-scale power storage.
Sodium-Sulfur Batteries
Sodium-sulfur (NaS) batteries are high-temperature batteries with high power density and efficiency. They are primarily used for utility-scale load balancing and grid support. These batteries operate at high temperatures and require special materials and safety considerations.
Solid State Batteries
Solid-state batteries are an emerging technology that replaces the liquid electrolyte in conventional batteries with a solid electrolyte. This adaptation offers several benefits, including higher energy density, more excellent safety, and longer life. While solid-state batteries are still in the developmental stage, they hold promise for the future of power storage.
Each battery storage space system has its advantages and limitations. Battery selection depends on application requirements, budget plans, and ecological considerations.
Why Lithium-Ion is the First Selection
Lithium-ion batteries have become the leading innovative technology in battery energy storage mainly due to the following advantages:
- High energy density: allows them to save more energy in both weight and volume. This makes them ideal for applications where space and weight are important considerations.
- Performance: Lithium-ion batteries typically have an energy efficiency of around 90-95%, indicating that only a tiny percentage of the energy is lost over the entire cost and discharge cycle. This high performance directly translates into reduced functionality costs over the battery system’s life.
- Cycle Life: Capable of withstanding hundreds or even countless charge/discharge cycles before capacity is significantly reduced.
- Cost Effectiveness: Although it has a higher upfront cost than other battery types, it is the perfect choice for long-term ownership.
| Battery Kind | Energy Density (Wh/kg) | Effectiveness (%) | Cycle Life (cycles) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Lithium-Ion | 150-250 | 90-95 | 2000-5000 |
| Lead-Acid | 30-50 | 70-80 | 200-300 |
| Nickel-Cadmium | 50-80 | 70-85 | 500-1500 |
- Low self-discharge rate: Only 2-3% of the cost is lost each month when not used. This is a much lower self-discharge rate than other batteries, which helps keep them on standby for long periods without regular recharging.
- Safety: Developing battery monitoring systems (BMS) and safety safeguard mechanisms minimizes the risk of thermal runaway and other hazards, making contemporary lithium-ion batteries safer than earlier products.
Together, these features have made lithium-ion batteries the preferred choice for various applications, from portable electronics to electric vehicles, and are increasingly becoming the preferred choice for real estate, commercial, and utility-scale power storage systems.
Commercial, Residential and Energy Scale Battery Energy Storage Space
Battery energy storage systems (BESS) are increasingly crucial throughout numerous commercial, household, and utility-scale markets. Each industry has distinct needs and advantages that these systems can supply, driving the fostering and development within the sector.
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Expense Cost savings | Lower electrical power costs by preventing peak need costs |
| Power Freedom | Minimized dependence on the grid |
| Back-up Power | Guaranteeing company continuity throughout outages |
| Advantage | Description |
|---|---|
| Power Security | Keeping power during grid interruptions |
| Eco-friendly Assimilation | Maximizing making use of solar and other renewable resources |
| Cost Effectiveness | Reducing electrical power costs through peak shaving and time-of-use prices |
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Grid Security | Supporting grid frequency and voltage regulation |
| Renewable Combination | Assisting in the addition of periodic renewable resource resources |
| Height Shaving | Decreasing the requirement for costly coming to a head nuclear power plant |
| Power Arbitrage | Purchasing low-cost power and selling it at higher rates |
To conclude, battery energy storage systems are crucial throughout all commercial, property, and utility applications. They use significant advantages that enhance energy efficiency, reliability, and integration with renewable sources, making them essential in our change to an extra sustainable and resistant energy future.